The study done by ( Spielberger,1972) defines anxiety as “an unpleasant emotional state or condition characterized by subjective feelings of tension, apprehension and worry and activation of arousal of the autonomic nervous system.” This definition above explains generalised anxiety and social anxiety is a type of anxiety. Social anxiety as defined by the Anxiety and Depression Association of America is “intense anxiety or fear of being judged, negatively evaluated or rejected in a social or performance situation.”
Review of Literature
1.Social Anxiety and Self Presentation: A conceptualisation model by Schlenker, Barry R, Leary, Mark R. (1982)
- “This study proposes that social anxiety arises when individuals are motivated to make a preferred impression on real or imagined audiences but perceive or imagine unsatisfactory evaluative reactions from subjectively important audiences.”
2.Shy children, phobic adults: Nature and treatment of social anxiety disorders Beidel, D. C., & Turner, S. M. (2007)
- “Social anxiety disorder occurs in children, adolescents and adults, but its manifestation and treatment differ depending on developmental factors.”
3.Cognitive factors that Maintain Social Anxiety Disorder: A Comprehensive Model and it’s treatment implications- Stefan G. Hoffman ( 2007 )
- “Social Anxiety Disorder ( SAD ) is a common, distressing and persistent mental illness. This model assumes that social apprehension is associated with unrealistic social standards and a deficiency in selecting attainable social goals. When confronted with challenging social situations, individuals with SAD shift their attention towards their anxiety, view themselves negatively as a social object, overestimate the negative consequences of a social encounter, believe that they have little control over their emotional response, and view their social skills as inadequate to effectively cope with their situation.”
4.Cognitive Components of Social Anxiety: An Investigation of the Integration of Self Presentation Theory and Self-Efficiency Theory - James E. Maddux, Larry W. Norton, Mark R. Leary ( 1988 )
- “The result of this study suggests firstly, social anxiety is related to low expectations regarding one’s ability to execute certain self-presentational behaviours and secondly that, socially anxious people may be characterized by pessimistic view of interactions in which others are not expected to respond favourably even when one’s behaviour is appropriate and successfully executed.”
5.Clinical Psychology Review, Volume 9, Issue 1,- New theoretical conceptions of Social Anxiety and Social Phobia- Peter Trower, Paul Gilbert ( 1989 )
- “It is argued in this paper that social anxiety arises from the activation of an evolved mechanism for dealing with intraspecies threat, a mechanism which has played a vital role in the evolution of social groups.”
6.Social Anxiety Edition 3, Clinical, Developmental and Social Perspectives. Chapter 20- Social Anxiety as an Early Warning System: A Refinement and Extension of the Self Presentation Theory of Social Anxiety- Mark R. Leary and Katrina P. Jomgman Sereno ( 2014 )
- Describes a refinement and extension of the self-presentational theory of social anxiety, which explains social anxiety in terms of people’s concerns with the impressions that other people are forming of them.
7. Interpretation Bias in Social Anxiety : A Dimensional Perspective- Jonathan D. Huppert, Edna B. Foa, Jami M. Furr , Jennifer C. Filip and Andrew Mathews. ( 2003 )
- Negative interpretation bias for social situations was positively related to social anxiety, but not to general negative affect. In contrast, positive social interpretation bias , was negatively related to general negative affect, and to a lesser extent, to social anxiety.
8.Clinical Psychology Anxiety Volume 22 Issue 7, Self focussed Attention in Social Phobia and Social Anxiety- Jane M Spurr and Lusia Stopa ( 2002 )
- According to the study, self-focused attention is an important maintaining factor in the disorder because it increases access to negative thoughts and feelings, can interfere with performance, and prevents the individual from observing external information that might disconfirm his or her fears.
9.Social Anxiety and Communication about the Self- Barry R. Schlenker and Mark R. Leary ( 1985 )
- Social anxiety appears to arise from people’s concerns of the impressions people are forming of them. It is proposes that social anxiety occurs when people are motivated to create a desired impression on audiences but doubt they will do so.
10.Responses to Social Exclusion: Social Anxiety, Jealousy, Loneliness, Depression and Low Self Esteem- Mark R. Leary ( 1990 )
- This social exclusion theory of anxiety proposes that a primary source of anxiety is perceived exclusion from important social groups.
Method
The research was done to study the impact of social anxiety on teenagers. The rationale of the study was due to my personal observations of how many teenagers around me and particularly a close friend of mine suffered because of their social anxiety and wanted to know how it impacts teenagers in today’s world. A short self created questionnaire on Google Forms was created and circulated amongst teenagers via Instagram and Whatsapp. The questions were short and straightforward and the sample size was between 35-40 teenagers aged between 14 and 19. The data remained anonymous and the participant only had to share their name if they felt the need to.
Results (Consent was taken from participants beforehand and they were informed why they are filling this form out)
The participants were also asked what they would do in a situation where they are encountering social anxiety to make themselves feel better.
1.Trying to calm yourself down and taking deep breaths
2.Find a person you know and cling to them. Pinch my forearm
3.breathing exercises
4.Take a deep breath and walk out
5.Self-motivation
6.My confidence has improved now but going to therapy and deep breathing always helps me. Usually in these situations I'm not able to control how I feel though.
7.I usually take deep breaths and try to calm myself down. It helps to take a friend or someone I know along with me because it makes me feel more comfortable.
8.Rationalising my thoughts about the situation usually helps me realise it's not a big deal and calm down, otherwise I usually just push through.
9.Count backwards, hug your knees , sit on the ground, drink a sip of water and stay alone for some time
10.I regulate my breathing and I reach out to people around me for support
11.I think of things that calm me down
12.I repeatedly tell myself that I'm okay. I stick with close friends or family members.
13.Usually like a slap/pinch to get me back to reality. It's usually fine after that.
14.Deliberate positive self-talk
15.Listen to music
16.Meditation
17.Take deep breaths to calm myself down
18.I usually take a break from what I’m doing
19.I try to calm myself down and tell myself they’re just people and nothing will happen. Even though the fear of people judging me doesn’t make things better I just try to clear my mind and take 3-4 deep breaths before entering
20.Dissociate
21.I've never found myself in a position where Social Anxiety has gotten the better of me, but I usually find taking the first step in the process of interaction the most important. If you can push yourself to start a conversation and listen to strangers, you can learn a lot from meeting new people.
22.I try calming my breath and clearing my mind.
23.I take deep breaths and tell myself what is causing me anxiety is temporary in the moment and I’ll soon go home and be comfortable.
24.I just take a breath and calm myself down by saying stuff like it doesn’t matter what people think and just continue
Interpretation and Discussion
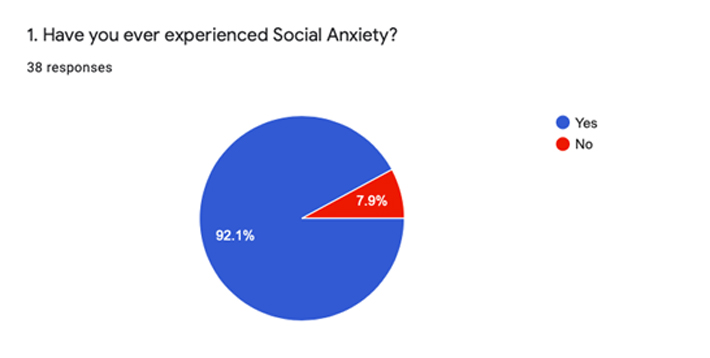
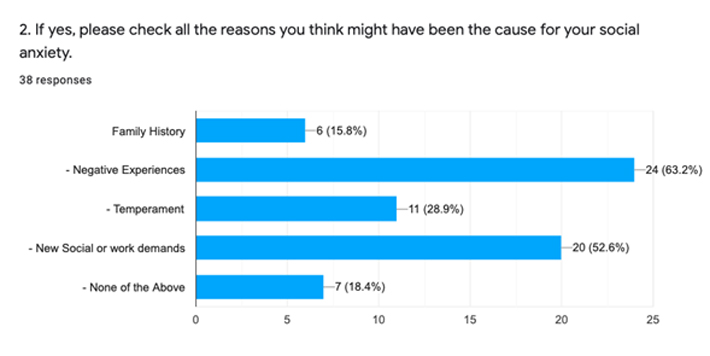
92.1% of participants said that they had experienced social anxiety at least once in their lives. Social anxiety might have been experienced because there was a lack of confidence and the participants thought that they wouldn’t live up to social standards. When asked what the participants think might have caused their social anxiety, 63.2% of participants said negative experiences. If the participant has had a prior negative social interaction, that would probably cause them to be anxious about their next upcoming social interaction and lower their confidence. 52.6% of participants also picked new social or work demands as a possible cause for their social anxiety.
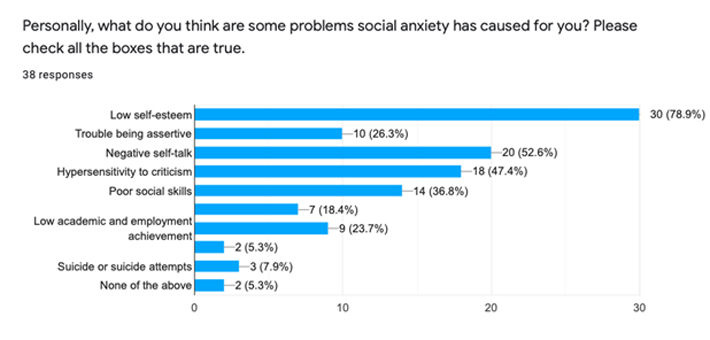
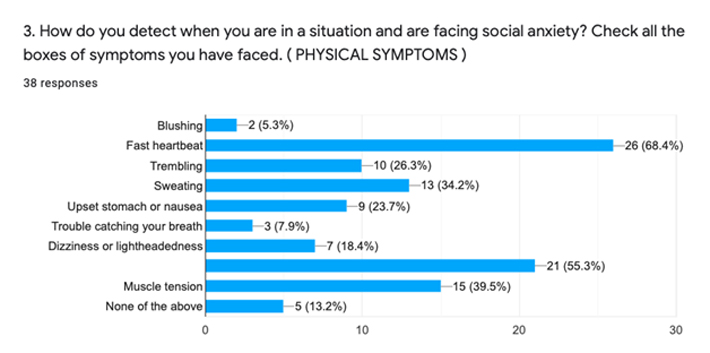
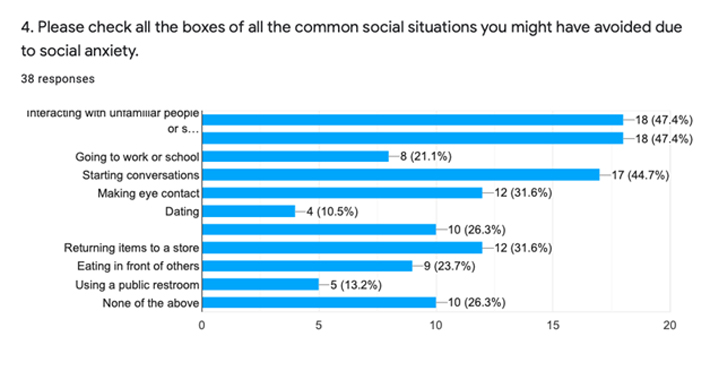
Participants must have thought new social or work demands are impacting their social anxiety as when they are put in a new and challenging environment and aren’t familiar with their surroundings or their fellow human beings, they might be anxious on how to start up a relationship with them and fit in. 78.9% of participants said that the biggest impact of social anxiety on them was low self esteem. The participants probably experienced feelings of low self esteem because they were put in a challenging social situation and they thought they didn’t perform as well as they should have, despite them dealing with the social situation perfectly. The physical impact of social anxiety that affected most participants was a fast and racing heartbeat. Participants said that they felt like their heart was violently pounding inside their chest. Some other prominent physical impacts of social anxiety that participants felt were that they felt like they blanked out, started sweating and felt their muscles getting tense. When asked what were some common social situations that they avoided due to their social anxiety, the most common response was interacting with unfamiliar people or strangers and avoiding going to parties and social gatherings. The participants might have avoided these scenarios since they both involve meeting and interacting with people who are not a part of your close circle/comfort zone. They could have been feeling anxious because they didn’t think they would be able to socialise as they were expected to and wouldn’t live up to everyone’s standards.
A few more similar scenarios that the participants avoided due to possibly the same reasons mentioned above were taking initiative and starting a conversation and making eye contact. One flaw in this study is that it can really be generalised. Some people might feel socially anxious only in some particular social settings such as dating and parties while they might be fine in other social settings such as school or work.
Implications
The results of this study could be possibly applied as a part of the curriculum in schools as a lot of people who suffer from social anxiety aren’t even aware that they suffer from social anxiety. If it is incorporated into the school curriculum then along with being aware of what they are suffering from, they can also learn how to calm themselves down when they are in a situation where they are facing social anxiety. Another benefit of awareness about social anxiety being incorporated into school curriculum is that people who don’t suffer from social anxiety will know how to behave around their peers who are socially anxious and it will teach them to be a little more sensitive towards socially anxious people.
Conclusion
The results of this study/research tell us that social anxiety as defined by the Anxiety and Depression Association of America is “intense anxiety or fear of being judged, negatively evaluated or rejected in a social or performance situation.” This study also tells us that that majority of our sample ( 38 teenagers ) suffers from social anxiety and the most prominent problem that social anxiety has caused for them is low self esteem and their heart starts pounding. Due to their social anxiety, the situations that the participants avoided the most were interacting with strangers and attending social gatherings. The results of this study could be included in the school curriculum to help spread awareness about social anxiety and the limitations of this research is that it could be very generalised at times.
References
https://adaa.org/understanding-anxiety/social-anxiety-disorder.
https://psycnet.apa.org/record/1983-05605-001.
https://psycnet.apa.org/record/2006-20311-000.
https://guilfordjournals.com/doi/abs/10.1521/jscp.1988.6.2.180.
https://guilfordjournals.com/doi/abs/10.1521/jscp.1990.9.2.221.
https://search.proquest.com/openview/846c7a6338343b9628083381082c8066/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=1819046.
https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/0261927x8543002.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/0272735889900445.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0272735802001071.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123944276000200.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1023/A:1026359105456.
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/16506070701421313.
Prarthana Batra is with Vasant Valley School